Upload a Bitmap Image and Save as a File in the Remote Backendless Storage.
At that place are several ways to upload file content to the server:
- The traditional approach where a concrete file from the client environment is uploaded using the API.
- Creating a remote file with content generated on the client-side.
In this commodity, we will review the first option – uploading a file with the API.
Once a file is uploaded, the File Service enables the post-obit:
- You can come across the file in File Browser in Backendless Console.
- The file can be downloaded via a URL assigned to information technology. The URL is equanimous as:
https://api.backendless.com/<application id>/<version name>/files/<path>/<file name>
- The application developer tin assign permissions to control who (users or roles) can download or delete the file.
- If git integration is enabled for the application; the file is also committed to the repository.
The case below demonstrates the API for file upload:
// create a file locally and so there is something to upload String filename = "myhelloworld-async.txt"; FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(filename); fileOutputStream.write("Hello mbaas!\nUploading files is easy!".getBytes()); fileOutputStream.shut(); terminal File file = new File(filename); // now upload the file Backendless.Files.upload(file, "/myfiles", new AsyncCallback() { @Override public void handleResponse(BackendlessFile uploadedFile) { Log.i(TAG, "File has been uploaded. File URL is - " + uploadedFile.getFileURL()); file.delete(); } @Override public void handleFault(BackendlessFault fault) { Log.e(TAG, error.getMessage()); } }); // create a file locally so at that place is something to upload val filename = "myhelloworld-async.txt" val fileOutputStream = FileOutputStream(filename) fileOutputStream.write("How-do-you-do mbaas!\nUploading files is easy!".toByteArray()) fileOutputStream.close() val file = File(filename) // now upload the file Backendless.Files.upload(file, "/myfiles", object : AsyncCallback { override fun handleResponse(uploadedFile: BackendlessFile) { Log.i(TAG, "File has been uploaded. File URL is - ${uploadedFile.fileURL}") file.delete() } override fun handleFault(fault: BackendlessFault) { Log.e(TAG, mistake.message) } }) // create a file data so there is something to upload NSData *data = [@"Hi mbaas!\nUploading files is easy!" dataUsingEncoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding]; // now upload the file [Backendless.shared.file uploadFileWithFileName:@"myhelloworld.txt" filePath:@"myfiles" content:data overwrite: YES responseHandler:^(BackendlessFile *uploadedFile) { NSLog(@"File has been uploaded. File URL is - %@", uploadedFile.fileUrl); } errorHandler:^(Fault *fault) { NSLog(@"Error: %@", mistake.bulletin); }]; // create a file information and then at that place is something to upload if let data = "How-do-you-do mbaas!\nUploading files is easy!".data(using: .utf8) { // now upload the file Backendless.shared.file.uploadFile(fileName: "myhelloworld.txt", filePath: "myfiles", content: data, overwrite: true, responseHandler: { uploadedFile in print("File has been uploaded. File URL is - \(uploadedFile.fileUrl ?? "")") }, errorHandler: { error in impress("Error: \(mistake)") }) } const Backendless = require('backendless') /* Or employ `import Backendless from 'backendless'` for customer side. If you don't utilize npm or yarn to install modules, you can add the following line <script src="//api.backendless.com/sdk/js/latest/backendless.min.js"></script> to your alphabetize.html file and apply the global Backendless variable. */ Backendless.initApp('YOUR_APP_ID', 'YOUR_JS_API_KEY') const handleFileSelect = event => { const { files } = outcome.target // FileList object for (let file of files) { Backendless.Files.upload(file, '/myFiles') .then(onSuccess, onError) } } const onSuccess = file => { panel.log('Uploaded file URL - ' + file.fileURL) } const onError = error => { panel.mistake('Server reported an mistake: ', error.message) console.error('mistake lawmaking: ', fault.code) console.fault('http condition: ', error.status) } // create a file locally and then at that place is something to upload Cord filename = "myhelloworld-async.txt"; File file = await File(filename).writeAsString("Howdy mbaas!\nUploading files is piece of cake!"); Backendless.Files.upload(file, "/myfiles").and so((response) { print("File has been uploaded. File URL is - " + response); file.delete(); }); When y'all run the code and the files are uploaded, you can meet them in Backendless Panel. To practise that:
- Login to Console, select your app and click the Files icon.
- You lot will run across the "myfiles" directory created by the lawmaking above. Click the directory name to see its contents.
- You should see two files as shown in the screenshot below.
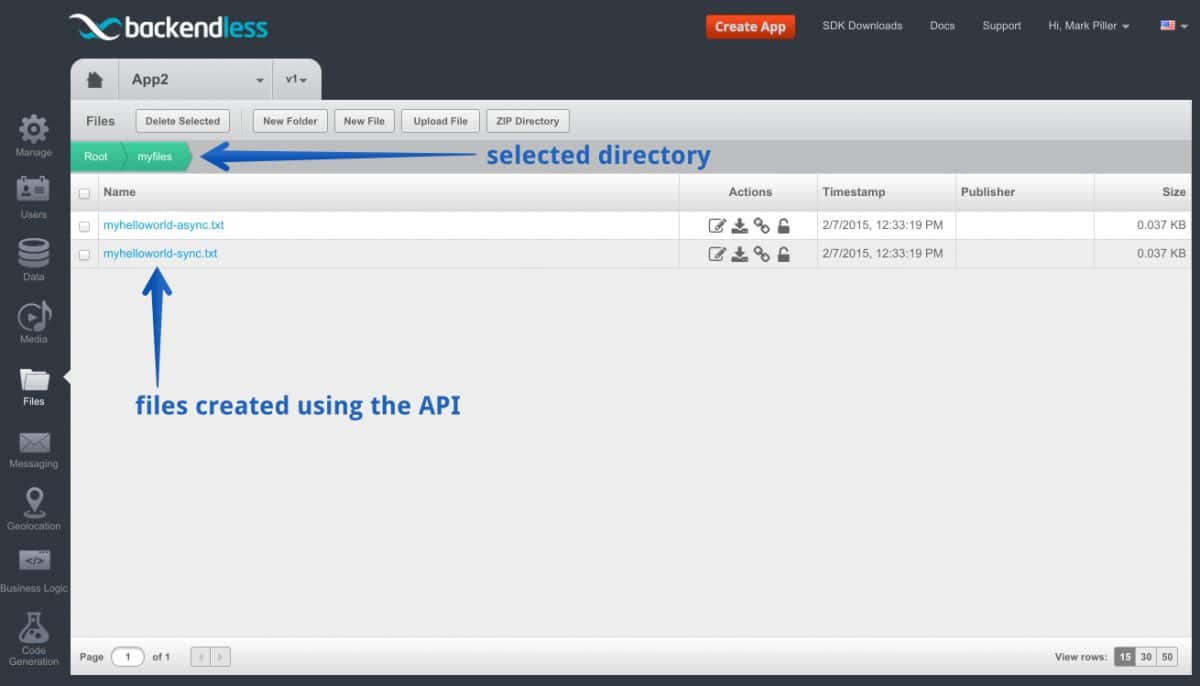
- To see the contents of the file, click the Edit file icon:
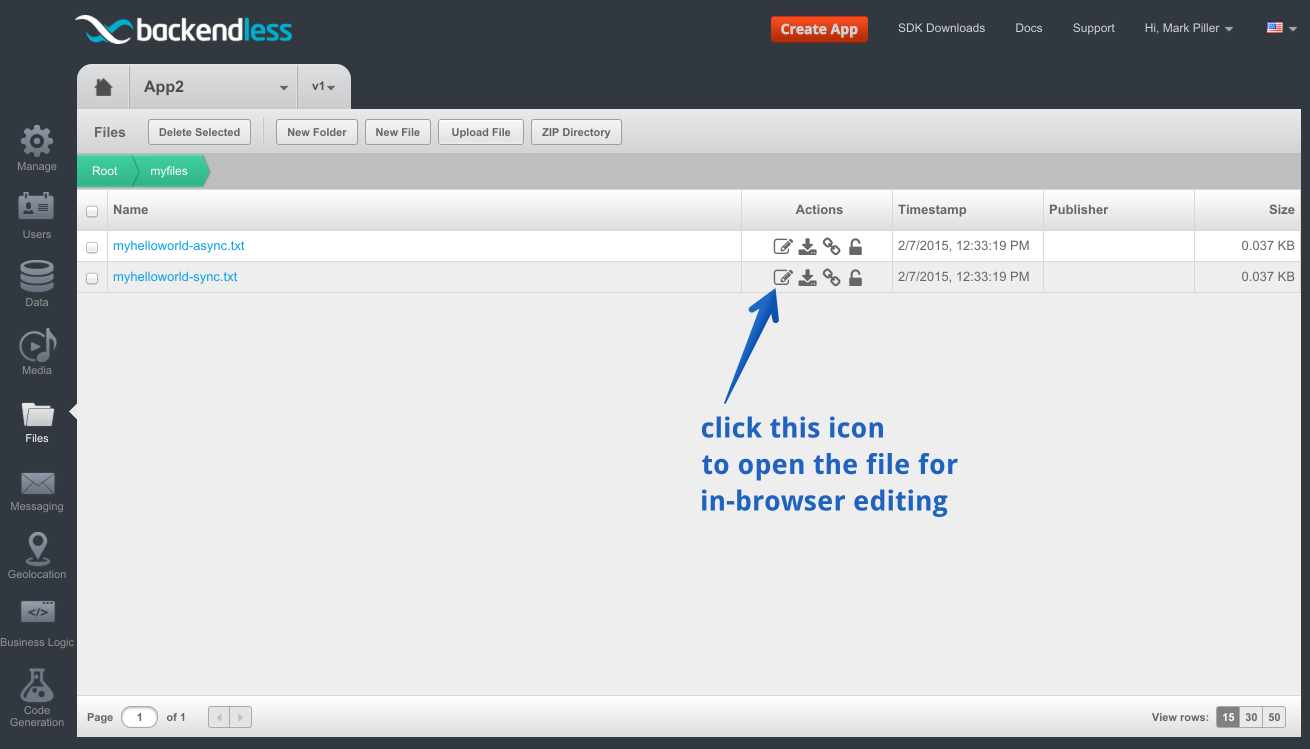
Enjoy!
Source: https://backendless.com/how-to-upload-files-to-server-with-file-upload-api/
Post a Comment for "Upload a Bitmap Image and Save as a File in the Remote Backendless Storage."